In the ever-evolving landscape of materials science, fiberglass tissue mat has emerged as a star player, revolutionizing numerous industries with its remarkable properties and diverse applications. This unassuming material, made up of randomly distributed glass fibers bonded together with an adhesive, has quietly become an integral part of our daily lives, from the cars we drive to the buildings we inhabit.
Understanding Fiberglass Tissue Mat
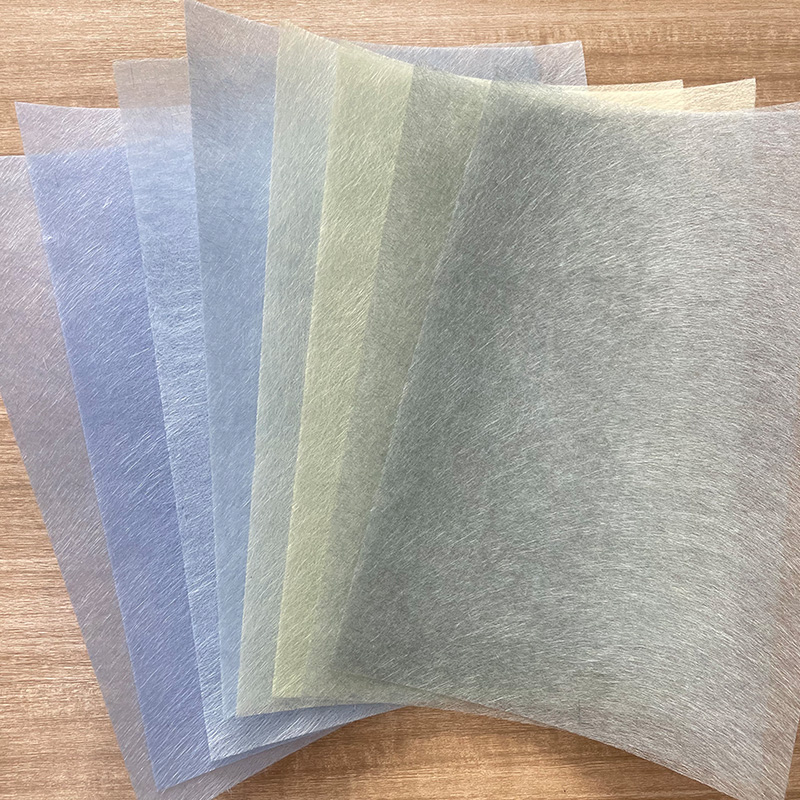
Fiberglass tissue mat is a type of nonwoven fabric that offers a unique combination of strength, durability, and flexibility. The glass fibers, which are typically very fine and lightweight, are arranged in a random pattern to create a mat-like structure. This random orientation gives the mat excellent isotropy, meaning it has the same properties in all directions. The adhesive used to bond the fibers together further enhances the mat's strength and integrity, ensuring it can withstand a variety of mechanical and environmental stresses.
One of the key advantages of fiberglass tissue mat is its high strength-to-weight ratio. Despite being incredibly lightweight, it can provide significant reinforcement to composite materials, making them stronger and more durable. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. Additionally, fiberglass tissue mat is highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and moisture, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.

Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, fiberglass tissue mat plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and safety of vehicles. It is commonly used in the production of body panels, hoods, and trunk lids, where it provides reinforcement to lightweight composite materials. By using fiberglass tissue mat, automakers can reduce the weight of these components without sacrificing strength, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Furthermore, fiberglass tissue mat is also used in the interior of vehicles, such as in the production of seat backs and headliners. Its excellent acoustic properties help to reduce noise and vibration inside the cabin, providing a more comfortable driving experience for passengers. In addition, the material's flame resistance makes it a safe choice for use in automotive interiors, helping to prevent the spread of fire in the event of an accident.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry has long relied on advanced materials to meet the demanding requirements of flight. Fiberglass tissue mat is no exception, and it is widely used in the construction of aircraft components. For example, it is used in the production of wing skins, fuselage sections, and engine cowlings, where its high strength and lightweight properties are essential for ensuring the structural integrity and performance of the aircraft.
In addition to its structural applications, fiberglass tissue mat is also used in the insulation of aircraft cabins. Its excellent thermal insulation properties help to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the cabin, while its fire resistance provides an added layer of safety. The material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures also makes it suitable for use in the engine and other high-temperature components of the aircraft.
Construction Industry
The construction industry is another major consumer of fiberglass tissue mat. It is used in a variety of applications, including the production of roofing materials, wall panels, and insulation products. In roofing, fiberglass tissue mat is often used as a reinforcement layer in asphalt shingles, providing increased strength and durability. It helps to prevent the shingles from cracking and splitting, extending their lifespan and improving the overall performance of the roof.
In the production of wall panels, fiberglass tissue mat is used to reinforce composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) panels. These panels are lightweight, yet strong and durable, making them ideal for use in both residential and commercial construction. Fiberglass tissue mat also plays a role in insulation products, such as fiberglass batts and blankets. Its excellent thermal insulation properties help to reduce energy consumption by preventing heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors.
Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry utilizes fiberglass tissue mat in a wide range of products, from consumer goods to industrial equipment. In the production of furniture, for example, fiberglass tissue mat is used to reinforce composite materials, such as those used in the construction of tabletops and chair frames. This helps to make the furniture more durable and resistant to wear and tear.
In the industrial sector, fiberglass tissue mat is used in the production of pipes, tanks, and other containers. Its corrosion resistance and high strength make it suitable for use in harsh chemical environments, where it can withstand the effects of acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances. The material is also used in the production of electrical insulation products, such as circuit boards and transformer coils, where its excellent electrical insulation properties are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical equipment.
Production Process
The production of fiberglass tissue mat involves several complex steps, each of which is carefully controlled to ensure the quality and consistency of the final product. The process typically begins with the production of glass fibers, which are made by melting a mixture of silica sand, soda ash, and limestone in a furnace. The molten glass is then extruded through a spinneret, which contains thousands of tiny holes, to form fine glass filaments.
These filaments are then gathered together to form a continuous strand, which is known as a roving. The roving is then chopped into short lengths, typically ranging from 3 to 50 millimeters, depending on the desired properties of the final mat. The chopped fibers are then mixed with an adhesive, which is typically a resin or polymer, and spread out on a conveyor belt to form a mat.
The mat is then passed through a series of rollers and ovens to cure the adhesive and bond the fibers together. The curing process typically involves heating the mat to a specific temperature for a certain period of time, depending on the type of adhesive used. Once the mat has been cured, it is cooled and wound onto a roll for further processing or packaging.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español