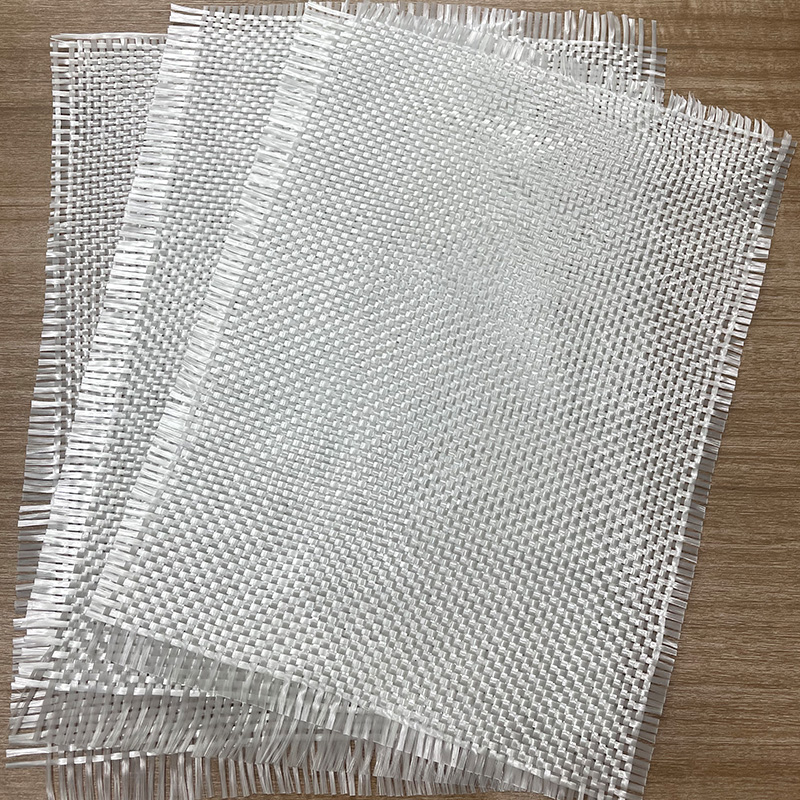
The strategic incorporation of specialized reinforcement materials is paramount in the realm of advanced composites manufacturing. Among these, the application of 275g Unidirectional Glass Fiber Cloth Fiberglass Cloth presents a distinctive opportunity to engineer components with highly targeted mechanical properties. This specific class of material, characterized by its concentrated fiber alignment and moderate areal weight, is not merely a filler but a foundational element that dictates the final structural integrity and performance profile of the composite laminate. Understanding the intricate balance between material characteristics, resin chemistry, and fabrication techniques is crucial for harnessing the full potential of this high-performance fabric.
The Fundamental Understanding of Unidirectional Fiberglass
The defining attribute of unidirectional glass fiber fabric is the near-exclusive alignment of its load-bearing fibers along a single axis, typically held together by minimal stitching or a light binder in the transverse direction. This deliberate orientation endows the resulting laminate with extraordinary high tensile strength and stiffness in that specific direction, a feature fundamentally different from the balanced properties of woven fabrics. The mechanical behavior is anisotropic, meaning the material's strength is directional, making it perfectly suited for structural elements subjected to primary loads along a predictable path, such as beams, spars, or stringers. Furthermore, the 275g per square meter (gsm) weight specification positions this material as a 'heavy' reinforcement when compared to lightweight surfacing veils, yet it remains manageable for multiple layer layups. This specific weight offers a substantial fiber volume fraction, translating directly into superior load-carrying capacity without leading to overly thick or unwieldy laminates that could complicate the infusion or wet-layup process. It represents a sweet spot for reinforcing moderately stressed components where weight control remains a factor, providing a denser concentration of fibers to absorb stress effectively.
Selecting the Optimal Resin System and Its Synergy
The final composite properties are as dependent on the matrix material as they are on the reinforcement, making Epoxy Resin Compatibility for 275 gsm Unidirectional Fiberglass a crucial consideration. Epoxy resins are often the preferred choice because of their excellent adhesive properties, low shrinkage during curing, and high mechanical strength, which allow them to effectively transfer stress between the tightly packed unidirectional glass fibers. When used in a wet layup or infusion process, epoxy's low viscosity typically ensures complete saturation and 'wet-out' of the dense 275gsm fabric, which is essential to prevent dry spots and maximize the material's tensile performance. Conversely, the applicability of **Vinylester and Polyester resins** requires careful assessment. While more cost-effective and faster-curing, these resins may exhibit higher shrinkage or a less tenacious bond with the glass fibers, potentially compromising the ultimate fatigue life and directional strength. They are generally suitable for less demanding applications like general marine repair or bulk reinforcement where chemical resistance or ultimate strength is not the absolute priority. The selection hinges entirely on the environmental exposure and the maximum stress levels anticipated for the finished structure.
Laying-up Techniques for Maximum Tensile Performance
To truly achieve superior structural outcomes, the lamination process must meticulously consider the Optimizing Flexural Stiffness with 275g Unidirectional Fiberglass Layering. The primary goal of using unidirectional fabric is the precise alignment of the high-strength fibers with the principal lines of tension or compression within the structure. This necessitates a strategic approach to ply orientation, often placing the 0° fibers parallel to the longest dimension or primary load path of the component. For complex structures, multiple layers might be used, where the first and last layers are aligned at 0° for maximum stiffness, while intermediate layers may be oriented at $\pm45^\circ$ or $90^\circ$ to provide necessary shear strength and hoop stress resistance. The technique of scientific stacking and the curing process is equally vital; consistent fiber tension during layup prevents wrinkling, and the application of moderate pressure during curing eliminates excess resin, leading to an optimal fiber-to-resin ratio. This ratio directly correlates with the final strength-to-weight performance of the cured laminate, transforming the material from a flexible cloth into a rigid, highly directional structural member.
Practical Applications in Specialized Industries
The unique mechanical profile of heavy unidirectional glass cloth finds its most compelling use in industries demanding high directional stiffness and load transfer efficiency. A prime example is Marine Stringer Reinforcement using Heavy Unidirectional Glass Cloth. Boat stringers and bulkheads are primarily subjected to longitudinal bending and compression loads, making the unidirectional fabric a perfect material to maximize strength along their length without excessive weight gain. The fibers are strategically placed along the stringer's axis, concentrating the load-bearing capacity precisely where it is needed. Beyond the marine sector, the material is also integral to the construction of wind turbine blades and performance sports equipment. In these applications, the fabric allows engineers to 'tune' the stiffness of the component, ensuring that the main fibers are aligned to withstand the extreme cyclic loads and bending moments experienced during operation, thereby enhancing durability and operational efficiency.
The Role as a Cost-Effective Alternative
In many engineering contexts, the 275g Unidirectional Fabric serves as an indispensable DIY Carbon Fiber Alternative 275g Unidirectional Fabric. While carbon fiber boasts superior specific strength and stiffness, its significantly higher material cost can be prohibitive for projects or products where budget constraints are tight. Unidirectional glass fiber provides a commendable balance, offering excellent directional properties at a fraction of the cost. The key is in the performance versus cost balance; for applications where the design criteria do not necessitate the ultimate stiffness of carbon fiber—or where the required factor of safety can be met with a slightly thicker, glass-reinforced section—the glass cloth offers a smart, economic substitute. This allows manufacturers and builders to achieve high-performance results without escalating material expenses, broadening the accessibility of advanced composite construction to a wider range of industrial and hobbyist projects.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español