Glass fiber mats are a staple in various industries, serving as critical components in applications ranging from construction to automotive and marine sectors. Two of the prominent types of glass fiber mats are chopped strand and continuous filament mats. Understanding the differences between these two materials can help manufacturers select the right type for their specific needs.
Introduction to Glass Fiber Mats
Glass fiber mats are made from woven or non-woven fibers that provide strength, durability, and resistance to various environmental conditions. These mats are often used as reinforcement in composite materials, enhancing the performance of products like boats, wind turbines, pipes, and automotive components. Glass fiber mats come in various forms, each designed for specific applications.
In general, the key factors influencing the choice of a glass fiber mat include its structure, fiber orientation, resin compatibility, and the intended end-use. Chopped strand and continuous filament mats are the two primary categories of glass fiber mats. Understanding their differences is crucial for determining which is the suitable for a given application.
What Is Chopped Strand Mat?
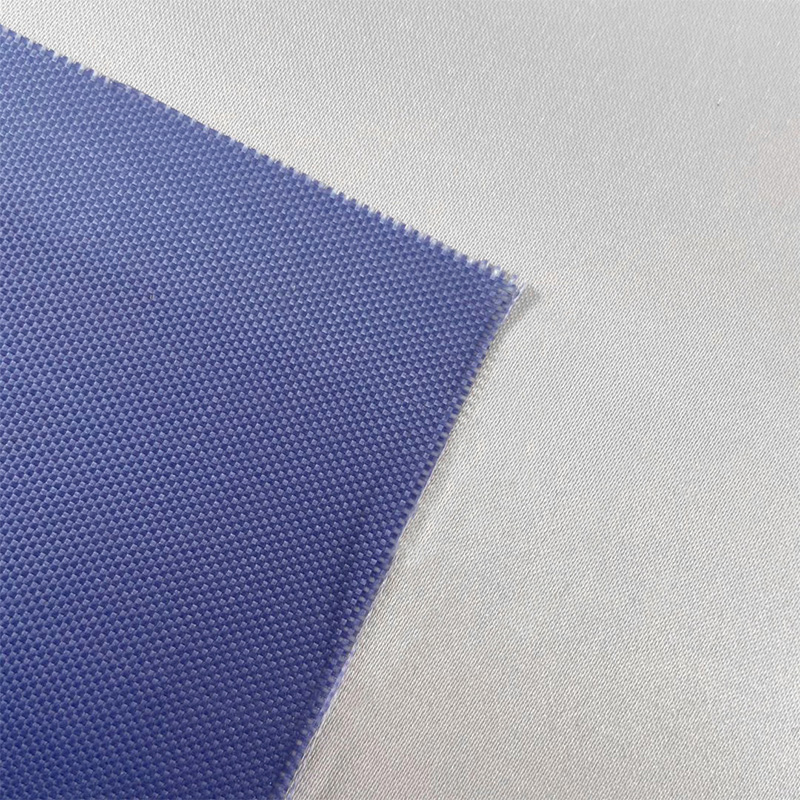
Chopped strand mats are made from short strands of glass fibers that are randomly distributed and bonded together with a resin. The fibers are typically cut into lengths of 25mm to 50mm and are held together by a binder, which helps maintain the mat’s structure. Chopped strand mats are versatile and easy to handle, making them suitable for various molding processes, including hand lay-up, spray-up, and compression molding.
Advantages of Chopped Strand Mat
- Ease of use: Chopped strand mats are relatively easy to handle and can be applied using a variety of molding techniques.
- Low cost: Due to the simplicity of the manufacturing process, chopped strand mats are typically more affordable than continuous filament mats.
- Good resin absorption: The random fiber orientation allows for efficient resin absorption, ensuring a strong bond with the matrix material.
- Flexible design: They are commonly used in applications that require flexibility and versatility, such as automotive parts and boat hulls.
Disadvantages of Chopped Strand Mat
- Lower strength and durability: While chopped strand mats offer good performance in general, they are typically less strong and durable than continuous filament mats due to their random fiber alignment.
- Limited application in high-performance environments: Chopped strand mats are less effective in applications that require high tensile strength or resistance to impact.
What Is Continuous Filament Mat?
Continuous filament mats, on the other hand, are made from long, continuous strands of glass fiber that are woven or stitched together to form a uniform mat. The fibers used in continuous filament mats are longer, providing improved strength and durability compared to chopped strand mats. These mats are commonly used in high-performance applications where structural integrity and resistance to wear and tear are critical.
Advantages of Continuous Filament Mat
- Higher strength: Continuous filament mats offer mechanical properties, including greater tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
- Better durability: The long fiber structure provides increased resistance to cracking and breaking, which is essential in environments exposed to harsh conditions.
- Uniformity: Continuous filament mats provide a more uniform structure, resulting in more consistent performance across large surfaces.
- Enhanced resin infusion: Continuous filament mats offer better resin infusion compared to chopped strand mats, resulting in a stronger bond and finished product.
Disadvantages of Continuous Filament Mat
- Higher cost: Continuous filament mats tend to be more expensive than chopped strand mats due to the more complex manufacturing process and the cost of raw materials.
- Less flexibility: While stronger, continuous filament mats are typically less flexible and may require specialized equipment to handle and process.
Key Differences Between Chopped Strand and Continuous Filament Mats
| Feature | Chopped Strand Mat | Continuous Filament Mat |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | Short, cut fibers (25mm to 50mm) | Long, continuous fibers |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Durability | Moderate durability | Superior durability |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Low flexibility |
| Cost | More affordable | More expensive |
| Resin Infusion | Good resin absorption | Better resin infusion |
| Application | General-purpose, low to moderate stress | High-performance, high-stress applications |
| Manufacturing Process | Simple, less complex | More complex, involves weaving or stitching |
Choosing the Right Type of Glass Fiber Mat
The choice between chopped strand and continuous filament mats depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as strength, flexibility, cost, and the nature of the manufacturing process all play significant roles in determining the appropriate material.
- For general applications such as automotive parts, boat hulls, and construction materials, chopped strand mats provide a cost-effective and versatile option. Their ability to be molded into complex shapes makes them ideal for a wide range of products.
Glass Fiber Mat Applications Across Industries
Glass fiber mats are used in various industries, each requiring different properties. Some of the primary applications of chopped strand and continuous filament mats include:
Automotive Industry
Both types of mats are used for automotive parts, including body panels, bumpers, and interior components. Chopped strand mats are often used for low-cost parts, while continuous filament mats are chosen for parts that require high strength and durability.
Marine Industry
Glass fiber mats are extensively used in boat hulls, decks, and other marine components. Continuous filament mats are preferred for high-stress areas, while chopped strand mats are used for general reinforcement.
Construction and Infrastructure
In the construction industry, glass fiber mats are used in reinforcing concrete, roofing systems, and insulation materials. Both types of mats are utilized, depending on the specific demands of the project.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both chopped strand and continuous filament glass fiber mats offer unique advantages depending on the specific needs of the application. Chopped strand mats are ideal for general-purpose applications where cost is a primary concern, while continuous filament mats are better suited for high-performance environments that demand strength and durability. By understanding the differences between these two types of glass fiber mats, manufacturers can make informed decisions about which material is suited for their projects.
FAQ
1. What is the primary difference between chopped strand and continuous filament glass fiber mats?
The main difference is the fiber length. Chopped strand mats use short, cut fibers, while continuous filament mats use long, continuous fibers, providing better strength and durability.
2. Can chopped strand mats be used in high-performance applications?
While chopped strand mats are versatile, they are generally not suitable for high-performance applications that require high strength and durability, such as aerospace or automotive structural components.
3. Which type of glass fiber mat is more cost-effective?
Chopped strand mats are typically more affordable due to their simpler manufacturing process compared to continuous filament mats.
4. What industries commonly use glass fiber mats?
Glass fiber mats are used across various industries, including automotive, marine, construction.
5. How do continuous filament mats enhance the resin infusion process?
The long fiber structure of continuous filament mats allows for better resin infusion, resulting in a stronger bond and more consistent performance in composite materials.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español